Requesting Permissions at Run Time Part 1
Android Run Time Permissions
In android marshmallow introduce the app permission feature that widely popular these days. If you are one of the android developers you should know it and think about to give support either for existing or older application.
Especially if you are targeting the latest android version that defiantly think about it, skipping this feature might be the cause to crash the application whenever it try to access those resource that denied by system or user.
Because beginning android 6.0 (API Level 23) user grant the permissions to app while it is running, not when installing or upgrading, It allow the user to more control over the resources, by going app’s Settings screen.
In short before access the resources application needs to check the permission from user either allow or deny developer should define the flow of the application. As per the officially developer design guide line said that your application should guide by showing the rational dialog to end user, why app require to access the resource? The user can revoke the permission any time it would be the app responsibility to again ask the permission.
System permissions are divided into two parts Normal and Dangerous.
Normal permission do not directly risk on user’s privacy. If your application lists a normal permission in its manifest file, the systems grant the permission automatically.
But the permission that can give the application to access the confidential data, if it is listed in app manifest file, the user has to explicitly give the approval to your app.
If you want to check the your permission is normal or dangerous. checking permissions
One question can defiantly raised that if you are targeting the latest version API 23 and app can handle the run time feature then what happens if installing in the same app in lower version device.
On all version of android, you need to declare both normal and dangerous permission its need to declare in your manifest file. However the effect of that declaration would apply depending on the system version and your application target SDK level.
-
If your application is targeting version 22 or lower and device is running android 5.1 or lower. If app uses the dangerous permission, the user has to grant the all permission while installing the app; if they do not allow the permission then system would not install the app at all.
-
If your app is targeting the version 23 or higher and device is running the android version 6.0 and higher version. The app has to list’s the permission in android manifest file and it must request each dangerous permission it needs while the application is running. This does not happen that if your app is installing then you received all permission. The app can continue to install and run with limited capabilities even if user denies a permission request.
Check for permissions
If your application uses dangerous permissions. App need to check whether you have permission every time when app performs the operation that requires the permission. The user can always revoke the permission even if app used the camera yesterday its means not app has till that permission today.
To check if you have permission, call the ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission() method. See the below snippet shows how to check if the activity has permission to write the calendar.
If application has the permission, the above method return PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED and app can processed the operation. If app does not have permission every time check it returns PERMISSION_DENIED and app has to explicitly ask the users for permission.
Request the Permissions
If your application needs a dangerous permission that listed in android manifest file, it must ask to user for grant that permission. Android provides the method for request the permission, calling this method bringing prompt the standard android dialog that cannot customize.
1. Explain why the app needs the permissions:
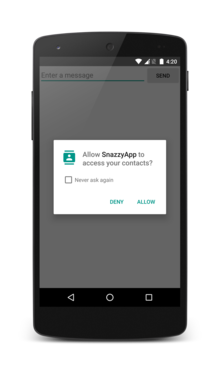
In some circumstances app need to help to user for understand why app need the permission. For example when user lunched one photography application, it would probably acceptable, if it ask to user for use the camera, but user might not understand why they want to ask the locations and contact permission. You should provide the explanation to user; keep in mind you should not overwhelm to user by providing more explanation. If you provide too many explanations, the user might find the app frustrating and remove it.
2. Request the permissions you need:
If your app does not have permission it needs, the app must call the requestPermissions() method to request the appropriate permissions.
Your app passes the permissions it wants along with the integer request code, that specify the unique identify the permission request.
This method works as asynchronies, it return the right way and after user response to the system dialog, the system call the callback method with the result, request code that passing while request for permission.
The following code snippet show app has contact permission and request the permission if necessary.
Notes if you call
requestPermissions()it bring the system dialog to use that your app can not configure alert dialog, if you need to show the additional dialog for explanation to the user, you should do this beforerequestPermission().
3. Handle the permissions request response:
When you app request for permissions, the system show the alert dialog to the user, when user response the dialog, the system invokes your override method onRequestPermissionResult(), along with response and request code. Your app must override this method for handle the response. This callback return that request code the passing at the time of requestPermission().
See the below example that shows the result of requested for READ_CONTACTS permission.
4. Permissions Best Practices:
Every time you ask to user for permission, it shows we force to users for make the decision we should minimize the number of make request for permission. Quite often your app can avoid to requesting by using intent instead. If feature is not core part of your app’s functionality should avoid to requesting the permission and use the other app calling the intent.
In many case you can choose between two ways to perform the same operation. You can have your app that ask the permission to perform the operation. Alternative using intent to have another app that can perform the task for your app.
For example your application needs to use the camera for capture the picture. Your app can have request the camera permission for use the camera inside your application. Your app directly accesses the camera API and captures the picture. This feature gives your application the overall control for handle the user interface. Another approach you app have intent that use the another app default camera that can handle the request for camera and perform the operation for you and result back to your application. This way you can minimize the requesting permission.
Your application should request for permission in each activity where your app needs, If the same request your app need in more than one place, you need to perform the requestPermission() and accept the resultPermission. In next post is how to request for the permission using RunTimeUtility class whenever needs from your activity and handle the response in your activity using it’s callback methods.
Android Marshmallow Permission Utility 2

